Table of Contents
By effectively utilizing both virtual and hardware routers, along with Tor and VPNs, users can significantly enhance their security, privacy, and anonymity. These tools provide essential protection against various cyber threats and offer peace of mind in today’s digital landscape. Ensure that the latest versions of software and firmware are used and adhere to best practices to maintain robust security.
Understanding the Use of Virtual and Hardware Routers in Security
Improving Security with Routers and Gateways
- Virtual Routers:
- Allow for the creation of isolated networks within a virtual environment.
- Enhance security by segmenting network traffic and providing additional layers of protection.
- Hardware Routers:
- Provide robust security features, such as firewalls and VPN support.
- Essential for filtering traffic and securing communication between devices on a network.
Utilizing Tor and VPNs
- Tor:
- Enables anonymous browsing by routing traffic through a series of encrypted nodes.
- Protects against network surveillance and traffic analysis.
- VPNs (Virtual Private Networks):
- Encrypts internet traffic and hides user IP addresses.
- Useful for securing data on public Wi-Fi and accessing restricted content.
Setting Up Secure Networks
- Combining Routers and VPNs:
- Configuring routers to work with VPNs adds an extra layer of security for all connected devices.
- VPN routers help maintain privacy across entire networks.
- Using Tor Routers:
- Tor-enabled routers route all connected device traffic through the Tor network, enhancing anonymity.
- Ideal for protecting privacy at the router level.
Key Considerations for Security
- Privacy and Anonymity:
- Combining Tor with VPNs can improve both privacy and security.
- Important to use reliable VPN services that do not log user activity.
- Configuring Security Features:
- Ensure routers are regularly updated with the latest security patches.
- Utilize strong passwords and network encryption standards like WPA3 for wireless networks.
- Additional Tools and Precautions:
- Use firewalls to prevent unauthorized access to networks.
- Implement intrusion detection systems for monitoring suspicious activities.
Setting Up VPNs and Tor on Routers
Overview
- Previously discussed setting up VPNs and Tor on the operating system.
- Now focusing on configuration on hardware and routers.
- Both VPNs and Tor can be established from the router, offering different advantages.
Differences and Benefits
- VPNs:
- Focused on privacy and security.
- Router can enforce traffic through an encrypted VPN tunnel from all devices on the network.
- Tor:
- Adds anonymity to privacy and security.
- Traffic routed through the Tor network to enhance user anonymity.
Setting Up on Routers
- VPN or Tor connections can be initiated from the internet router.
- Portable routers can provide security while traveling.
- All internet traffic is routed through these encrypted tunnels, reducing leaks.
VPN Client Setup
- Even on routers, VPN is referred to as a client.
- VPN client settings are required for setup, e.g., on DDWRT.
Pros of Using Routers for VPNs and Tor
- Comprehensive Traffic Encryption:
- All network traffic goes through the encrypted tunnel.
- Physical isolation from malware attempting to detect actual IP addresses.
- Protection While Traveling:
- Portable routers encrypt traffic, safeguarding against local attacks.
Cons of Using Routers for VPNs and Tor
- Potential for Leaks:
- Connection drops could lead to data leaks.
- Incorrect configuration may leak DNS or IPv6 information.
- Lack of Stream Isolation (Tor):
- Transparent proxying lacks stream isolation, causing shared circuits/IPs for users.
- Risks correlation of different aliases by observers.
- Security Concerns:
- Purchased black-box solutions may lack transparency in security setups.
- State actors could target these devices for interdiction.
- Browser Security Needs:
- Tor browser benefits are lost; a hardened browser is necessary.
- Hardened browsers are essential for maintaining high levels of privacy.
- Potential Targeting of Privacy Routers:
- Known to be used for privacy/anonymity, could be targeted for backdoors.
- Documented cases of such interdictions exist.
- Inherent Weaknesses:
- VPN and Tor protocol weaknesses apply to router implementations as well.
Shellfire Box – VPN Router Evolution
Using Routers with Custom Firmware for VPN, Tor, and SSH Gateways
Custom Firmware Options
- OpenWRT:
- Supports OpenVPN for VPN setup.
- Libra CMC and DDWRT:
- Both are options for custom firmware.
- Example of open client configuration is shown with DDWRT.
Benefits of Using Routers for VPN/Tor
- Centralized security management for all network traffic.
- Ability to configure router to route all or specific traffic through the VPN/Tor.
Pre-Flashed Routers
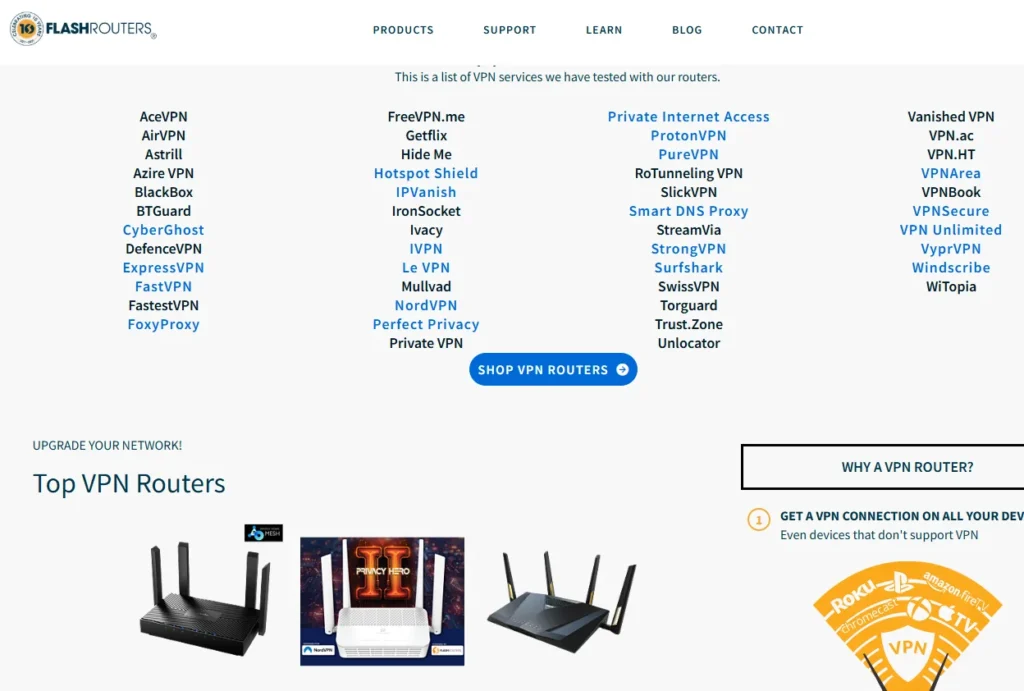
- FlashRouters.com offers routers pre-loaded with VPN configurations.
- These provide a simplified setup to avoid the complexity of flashing firmware.
- Customers can select routers based on VPN provider compatibility.
Manual VPN Client Setup
- Users can manually configure a VPN client on the router.
- Allows routing of all or selective network traffic through VPN based on user-defined conditions.
- Example: Configuring OpenVPN client settings on DDWRT with necessary credentials and configurations.
Tor Setup on Routers
- Advantages:
- Ability to Torify device traffic or entire network traffic through Tor.
- Option to set up as SOX-5 proxy for higher stream isolation or as a transparent proxy.
- Challenges:
- Requires understanding of IP tables and routing configurations.
- Mistakes can lead to potential data leaks, emphasizing the need for expertise.
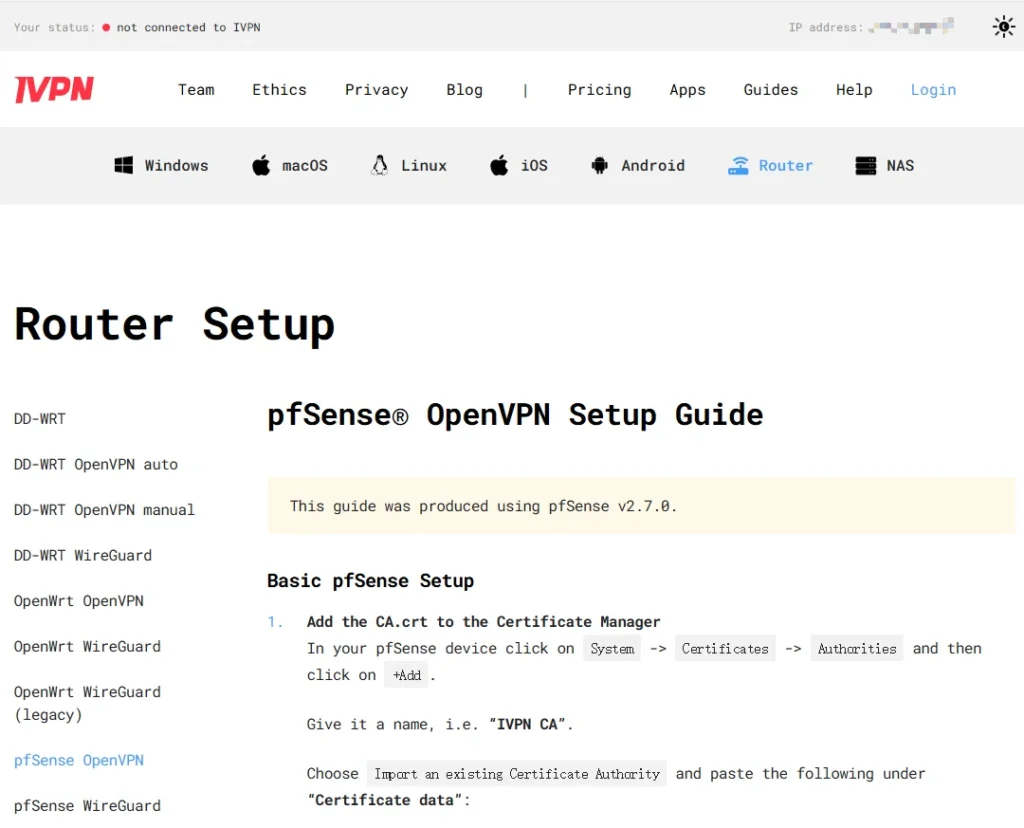
PFSense as an Alternative
- Overview:
- Free open-source firewall software based on FreeBSD.
- Installed on a computer to act as a dedicated firewall and router.
- Advantages:
- Easier to set up as a VPN client and Tor gateway compared to others.
- Offers robust security and ease of use.
- Resources:
- Provides guides for setting up both Tor gateways and VPN clients on PFSense.
Considerations
- Be cautious as incorrect configurations can lead to security vulnerabilities.
- Pre-flashed routers or services like PFSense may offer simpler solutions for those less technically inclined.
- Always refer to provider and firmware documentation to ensure accurate and secure setup.
Off-the-shelf VPN and Tor Routers
Overview
- Purpose:
- These routers offer ready-made solutions for establishing VPN or Tor connections.
- Useful for both home networks and traveling, providing security and privacy.
- Connectivity:
- Can connect via Ethernet (LAN port) or Wi-Fi.
- Acts as an intermediary between your devices and the internet.
- Power Source:
- Powered by USB, AC adapter, or batteries, depending on the model.
Uses and Benefits
- Travel Security:
- Protects against local hackers by encrypting local traffic, ideal for using on public Wi-Fi.
- Home Use:
- Can be integrated into home networks to secure traffic via VPN or Tor.
- Functionality:
- Provides VPN/Tor tunneling for all or selected traffic.
- Some are designed for easy plug-and-play, lacking configurability, suitable for mass-market use.
Considerations
- Service Provider Evaluation:
- Check the pre-configured VPN service against key criteria for suitability.
- Router Features:
- Determine if routers support specific Tor features, such as bridges or pluggable transports.
- Assess how customizable and user-friendly they are.
- Potential Issues:
- Must test for vulnerabilities, such as DNS leaks, IPv6 leaks, and handling of VPN/Tor dropouts.
- Evaluate risk of interdiction and backdoors based on personal security needs.
Available Options
- Tiny Hardware Firewall:
- Comes with one-year VPN service subscription.
- Offers OpenVPN and Tor functionality.
- Variants with increased range and compactness are available.
- Primarily for protection against local hackers.
- InvizBox:
- Offers a Tor router and a VPN travel router.
- Supports older pluggable transports, lacking OBS 4.
- VPN router includes 12 months of VPN access.
- Anonabox:
- Includes routers supporting Tor, VPN, and both.
- Some models support Tor bridging and relays.
- Safe Plug:
- Tor router option, not portable, without pluggable transports.
Building Your Own Tor Router
Portal Project
- Overview:
- Portal stands for Personal Onion Router to Assure Liberty.
- Developed by The Grook, Ryan Octal, and Mark C. Junkie, respected figures in security.
- Features:
- Provides full Tor support with pluggable transports and voice capabilities.
- Protects against leaks and offers fail-safe features for connection drops.
- Setup:
- Flash compatible off-the-shelf routers with Portal firmware, based on OpenWRT.
- Recommended routers include portable options known to work with Portal.
- One option is the gi.net smart router, a clone with Tor and OpenWRT pre-installed.
- Consider obtaining hardware from sources like China to avoid potential backdoors.
- Considerations:
- Portal project has not been updated recently, but users with technical expertise can maintain updates themselves.
Onion Pi Project by Adafruit
- Overview:
- A portable Tor solution using a Raspberry Pi.
- Acts as a learning project, ideal for those wanting hands-on experience.
- DIY Approach:
- Provides guidance for creating a Tor router using Raspberry Pi.
- Encourages exploration and learning in building your own privacy-focused router.
DIY Tor Router Options
- Using DD-WRT or PFsense:
- Allows full customization of a Tor router.
- Suitable for those who want a completely tailored solution.
- Considerations:
- Requires a good understanding of networking and security.
- Offers high flexibility but demands more technical skills.
Building your own Tor router can significantly enhance your online privacy and security. Whether through established projects like Portal and Onion Pi or a fully DIY approach with DD-WRT or PFsense, these solutions provide varying levels of customization and learning opportunities. Be sure to maintain updates and security practices to ensure optimal protection.
Virtual Gateways for VPN and Tor
Introduction
- Physical vs. Virtual Gateways:
- Discussed physical VPN and Tor routers and gateways.
- Virtual gateways offer flexibility and can be used with various workstations.
Hoonix Gateway
- Compatibility:
- Works with Hoonix workstation and any other VM configured correctly.
- Security Features:
- Provides security features for torrifying internet connections.
- Setup Example:
- Hoonix gateway configured with NAT and internal network settings.
- Debian client VM connected to the internal network using static IP addresses.
- Advantages:
- Well-designed for Tor, offering isolation and security.
- Virtualization adds an extra layer of protection.
Physical Gateway Options
- Portal:
- Recommended physical gateway option.
- Hoonix on Physical Device:
- Hoonix can also be installed on a physical device for added security.
PFSense as a Virtual Gateway
- Functionality:
- Can be used as a virtual gateway for both Tor and VPNs.
- Setup:
- Similar setup to Hoonix workstation, with NAT and internal network configurations.
- Devices connect via DHCP by default.
- Resources:
- Links provided for setting up Tor and VPN clients on PFSense.
RAS Tor Gateway VM
- Overview:
- OpenWRT-based router VM providing Tor connections using Transproxy.
- Setup Process:
- Download script and VM OVA file, run script, import OVA into VirtualBox.
- Use Cases:
- Lightweight use or testing purposes.
- Availability:
- Available for download, though not recently updated.
Virtualization Benefits:
- Virtual gateways offer a viable option for Tor and VPN through virtualization.
- Provides flexibility and security for various use cases.
Creating the Ultimate Tor Virtual Network
Conclusion
Virtual and hardware routers play a critical role in enhancing security, particularly when combined with VPNs and Tor for network traffic encryption and anonymity. Virtual routers create isolated networks within virtual environments, while hardware routers provide essential security features like firewalls and VPN support. Setting up VPNs and Tor on routers ensures all traffic is encrypted, offering comprehensive protection across entire networks.
Pre-configured routers from services like FlashRouters and open-source firmware like DD-WRT and PFSense allow for customizable and secure network solutions. Building your own Tor router with projects like Portal or Onion Pi provides heightened privacy and control over your online activities. However, due to network issues, the specific URLs provided could not be successfully parsed;
it is recommended to verify the legitimacy of the web addresses and retry the request. Despite this, the information above offers a comprehensive understanding of how routers can be utilized to secure and anonymize internet connections.